Hidradenitis Suppurativa
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
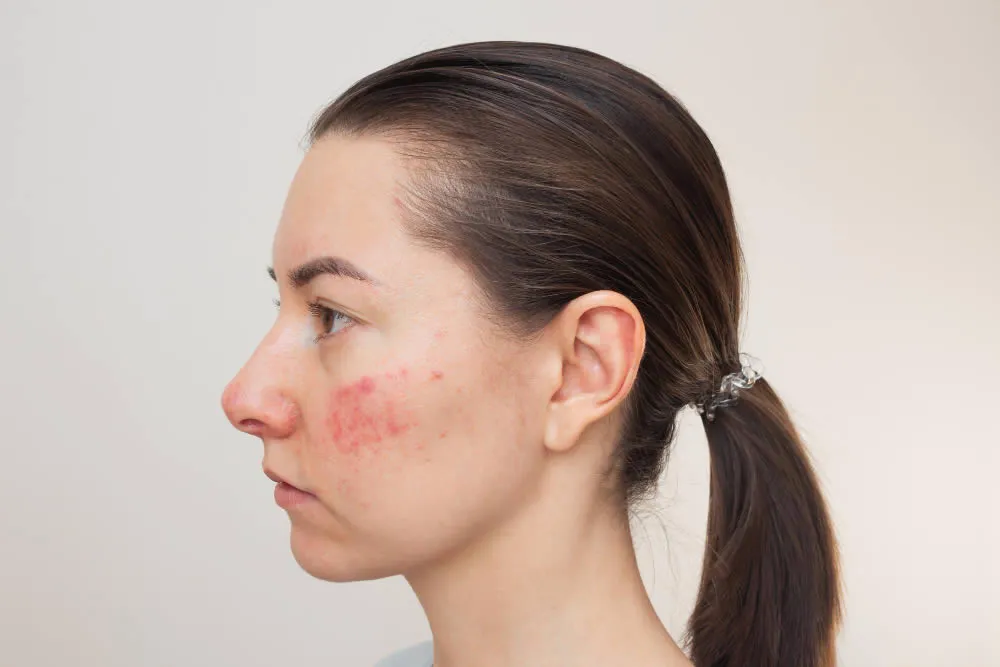
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a long-term skin condition that causes painful bumps under the skin, usually in areas where the skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks and breasts. The bumps can break open and drain pus, and sometimes form tunnels and scars under the skin. The condition is thought to be related to the inflammation of the hair follicles and sweat glands. The exact cause is unknown, but some factors that may trigger or worsen it include smoking, obesity, hormonal changes, stress and genetics. There is no cure for hidradenitis suppurativa, but treatments can help manage the symptoms and prevent complications. These include antibiotics, steroids, hormonal therapy, biologics and surgery.

What are the signs and symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Some of the signs and symptoms of hidradenitis suppurativa are:
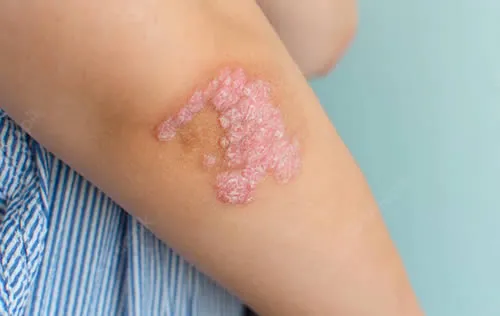
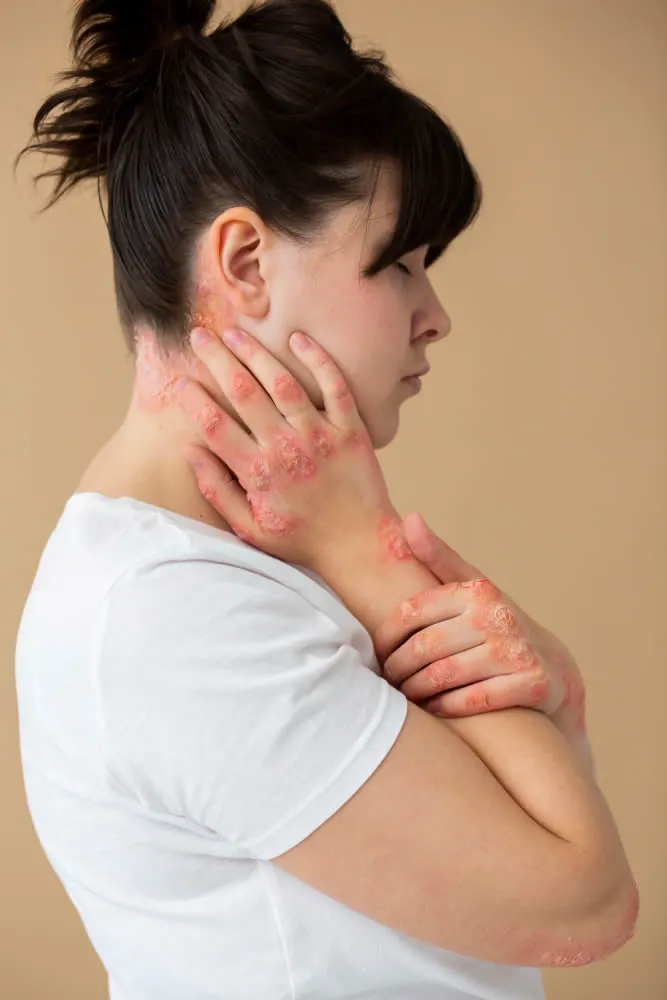
- Blackheads that appear in small, pitted areas of skin, often in pairs
- Painful pea-sized lumps that form under the skin, usually in areas where the skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks and breasts
- Leaking bumps or sores that break open and drain pus with an odor
- Tunnels that form under the skin, connecting the lumps
- Scars that result from the healing and reopening of the wounds
The severity and frequency of the symptoms may vary from person to person. Some people may experience only mild symptoms, while others may have chronic and painful outbreaks. The symptoms may also flare up and subside over time.
What are the causes of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is unknown, but it is thought to be related to the inflammation of the hair follicles and sweat glands. Some factors that may trigger or worsen hidradenitis suppurativa include:
- Smoking cigarettes, which is the most common trigger for hidradenitis suppurativa
- Being overweight or obese, which increases the risk and severity of hidradenitis suppurativa
- Hormonal changes, such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause
- Stress, which can affect the immune system and inflammation
- Genetics, as some people may inherit a tendency to develop hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa is not an infectious or contagious disease, and it is not caused by poor hygiene or diet. However, keeping the skin clean and avoiding irritants may help prevent flare-ups.
What treatments are available at the dermatologist for Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Some of the treatments that are available at the dermatologist for hidradenitis suppurativa are:
- Medications: These include antibiotics, steroids, hormonal therapy, biologics, and retinoids. They can help reduce inflammation, infection, and pain, as well as prevent new lesions from forming.
- Surgery or other procedures: These include incision and drainage, excision, skin grafting, laser therapy, and radiotherapy. They can help remove or destroy the affected tissue, drain the pus, and improve the appearance of the scars.
- Skin care: This involves using a wash with benzoyl peroxide and switching to a gentle antiperspirant. This can help prevent or reduce flare-ups and complications.
The best treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa depends on the severity and extent of the disease, as well as your personal preferences. You should consult with your dermatologist to find a treatment plan that suits your needs.

FAQ About Hidradenitis Suppurativa
How is hidradenitis suppurativa diagnosed?
Is hidradenitis suppurativa contagious?
No, hidradenitis suppurativa is not contagious. You cannot catch it from someone else or spread it to other people. HS is not an infectious or sexually transmitted disease. It is caused by an abnormal immune response that affects the hair follicles and sweat glands in certain areas of the skin.
Is hidradenitis suppurativa related to other diseases?
Yes, hidradenitis suppurativa is related to other diseases. People with HS have a higher risk of developing other conditions that are associated with inflammation or immune system dysfunction.
Is there a dermatologist near me in Arlington that offers treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa?
Yes. At our Arlington dermatology office we offer treatment for Hidradenitis Suppurativa to patients from Arlington and the surrounding area. Contact our office today to schedule an appointment.